DiYES International School – Cheek swelling in children can be both alarming and confusing for parents. This condition may arise from several different causes ranging from harmless teething discomfort to more serious infections. While some cases resolve naturally others may require medical intervention. The most important step is to observe the child’s symptoms closely including the presence of fever tenderness redness or unusual behavior. A child who develops a swollen cheek might experience trouble chewing sleeping or even speaking. Parents should not immediately panic but must pay attention to how quickly the swelling develops and whether other symptoms accompany it. Prompt action helps avoid complications and ensures appropriate care. In some cases cheek swelling is linked to oral problems like an infected tooth or a gum abscess. In others it might be due to allergic reactions or even skin-related disorders. Understanding the common triggers for facial inflammation in children helps parents make informed decisions and seek help when necessary.
One of the leading causes of cheek swelling in children involves dental infections. When a child has an untreated cavity or a cracked tooth bacteria may enter the pulp and spread to the surrounding tissues. This often leads to abscesses that result in visible swelling of the cheek especially on one side. Cheek swelling in children caused by dental problems may also be accompanied by sensitivity to heat or cold bad breath or refusal to eat. Swelling may develop gradually or appear suddenly and is often painful to the touch. If left untreated the infection can spread to the jawbone or further into the facial muscles which may result in more serious health risks. Dental abscesses in children must be treated promptly by a dentist who may perform drainage or prescribe antibiotics. Routine dental check-ups help prevent such problems before they develop into painful conditions requiring urgent care.
“Read about: Swollen Gums in Kids: When to Worry and What to Do”
Aside from dental origins cheek swelling in children can also result from sinus infections. This type of swelling is more common in older children especially those who have frequent colds or allergies. The sinuses are located behind the cheeks nose and eyes and when they become inflamed pressure can build up in the face. This may lead to puffiness around the cheeks and eyes and discomfort when the child bends over or lies down. The child may also experience nasal congestion headaches or fatigue. Unlike a dental abscess sinus-related swelling usually affects both sides of the face although not always equally. In many cases this inflammation follows a viral infection or prolonged exposure to allergens like dust or pollen. While some mild cases resolve on their own persistent symptoms may require decongestants or antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis helps prevent the progression to more serious sinus conditions or complications such as orbital cellulitis.
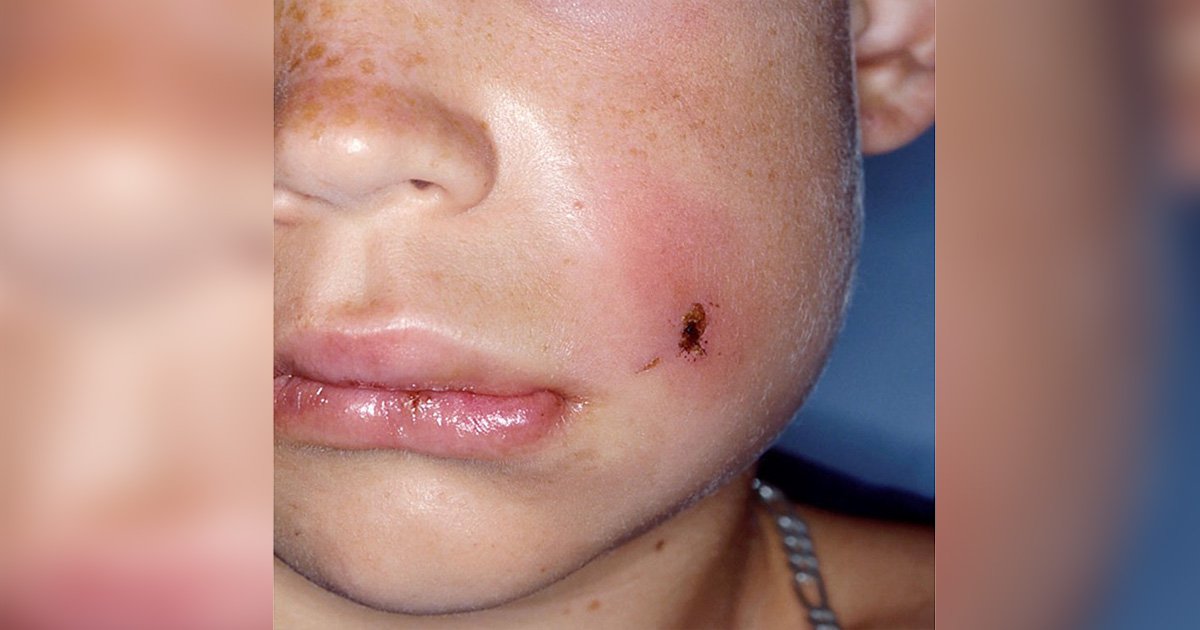
Cheek swelling in children can sometimes be related to skin conditions or allergic reactions rather than infections. Conditions like eczema or contact dermatitis may cause the cheeks to appear red itchy or slightly swollen. These reactions are usually triggered by skin contact with irritants such as fragrances soaps or certain fabrics. Allergies to food pollen or pet dander can also cause facial inflammation. Children with sensitive skin are especially prone to these issues. In addition insect bites may lead to local swelling especially when scratched repeatedly. In rare cases a more serious allergic reaction such as angioedema may cause rapid swelling which requires immediate medical attention. Most skin-related swelling responds well to antihistamines or topical treatments but it is important to identify the exact cause to prevent future episodes. Proper skin care and allergy management can reduce the frequency and severity of these flare-ups and improve the child’s overall comfort and confidence.
Though some cheek swelling in children resolves without medical treatment there are certain signs that should not be ignored. If the swelling increases rapidly becomes more painful or is accompanied by fever vomiting or trouble breathing immediate medical help should be sought. Health professionals can evaluate whether the cause is bacterial viral allergic or mechanical in nature. They may conduct a physical exam imaging or lab tests to determine the best course of action. In cases where an infection is identified antibiotics or drainage may be necessary. Parents should avoid pressing on or applying unknown creams to the affected area unless directed by a doctor. Comfort measures such as cold compresses and keeping the child hydrated are usually safe. Awareness of these guidelines helps families act confidently during such episodes. Recognizing the patterns and symptoms of cheek swelling in children can reduce anxiety and promote quicker healing for the young patient.