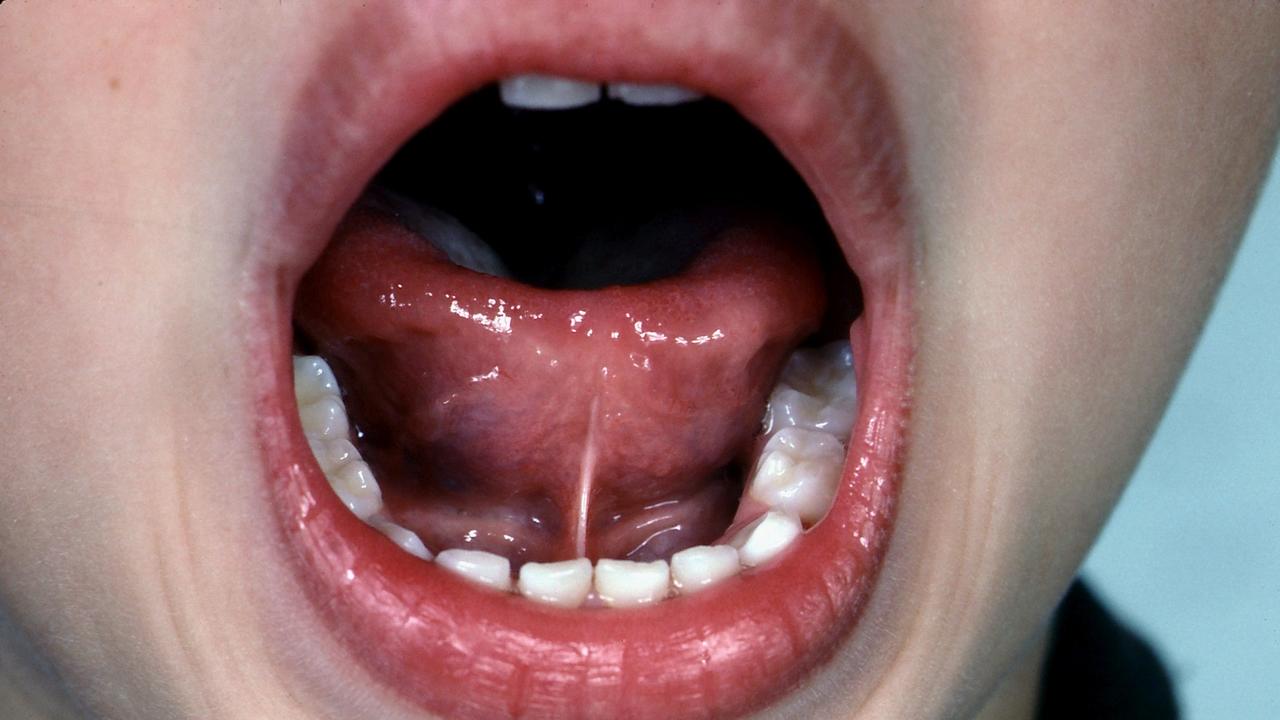
DiYES International School – Tongue Tie, also known as ankyloglossia, is a condition that affects the movement of the tongue. It occurs when the band of tissue under the tongue is shorter than usual. This condition can restrict the tongue’s movement, leading to difficulties in breastfeeding and speaking. In some cases, it can also affect a child’s oral hygiene. Parents should be aware of the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for this condition.
Tongue Tie, or ankyloglossia, is a congenital condition that affects babies and young children. It is characterized by a tight or restricted frenulum, the tissue that connects the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. This restriction limits the tongue’s range of motion. The severity of tongue tie varies from mild to severe. In some cases, it may not cause significant issues. However, in more severe cases, it can impact a child’s ability to breastfeed and speak clearly.
“Read about: Roseola in Children: Symptoms, Treatment, and Care Tips”
The symptoms of tongue tie can differ depending on the severity of the condition. In newborns, common signs include difficulty latching onto the breast during breastfeeding. This can lead to poor weight gain, fussiness, and frustration during feedings. Some babies may make clicking noises while feeding, which indicates a poor seal. As children grow, tongue tie can cause problems with speech. For example, they may have trouble pronouncing certain sounds, such as “t,” “d,” or “l.” It may also lead to dental issues, such as difficulty cleaning the teeth properly.
This condition happens when the frenulum, the tissue under the tongue, is unusually short or thick. It is typically present at birth. The exact cause remains unclear, though it is often linked to genetic factors. If a close relative has experienced a similar issue, the likelihood increases in other family members. In certain cases, environmental influences may also play a role in its development.
“Read more: Tackling the Root Causes of Human Trafficking in Africa: A Comprehensive Approach”
In many cases, tongue tie resolves on its own as a child grows older. However, in cases where the condition causes significant issues, treatment may be necessary. The most common treatment for tongue tie is a procedure called a frenotomy. During a frenotomy, a healthcare professional will snip the frenulum to release the restriction. This procedure is quick and typically done without anesthesia, especially in infants. After the procedure, the child may experience some discomfort, but the recovery time is usually short.
In more severe cases, a frenuloplasty may be recommended. This is a more complex procedure that involves surgically repositioning the frenulum to allow for greater tongue movement. This procedure may be performed in older children or adults who experience ongoing difficulties with tongue movement.
In some cases, children with tongue tie may benefit from speech therapy. This therapy can help children improve their ability to make certain sounds and improve their overall speech clarity. A speech-language pathologist will work with the child to teach them exercises and techniques to strengthen the tongue and improve speech. Speech therapy may be especially helpful if the child has difficulty with articulation due to the limitations of tongue movement.
Parents should consult a pediatrician if they notice restricted tongue movement in their baby or child. In newborns, difficulty latching onto the breast or poor weight gain may indicate a problem. If a child struggles with speech or faces eating challenges, seeking professional help becomes essential. A pediatrician or dentist can assess how limited the movement is and decide if treatment is needed. In some cases, early action can prevent more serious speech or feeding issues as the child grows.
Unfortunately, there is no known way to prevent tongue tie, as it is a congenital condition. However, early detection and intervention are key to minimizing any long-term effects. Parents should monitor their child’s feeding and speech development. If any issues arise, they should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action.