DiYES International School – Gallstones in children are uncommon but can still occur. Gallstones are hard deposits that form in the gallbladder. They can cause pain and discomfort. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for parents. Early intervention can help manage the condition effectively. This article explores gallstones in children and provides valuable insights.
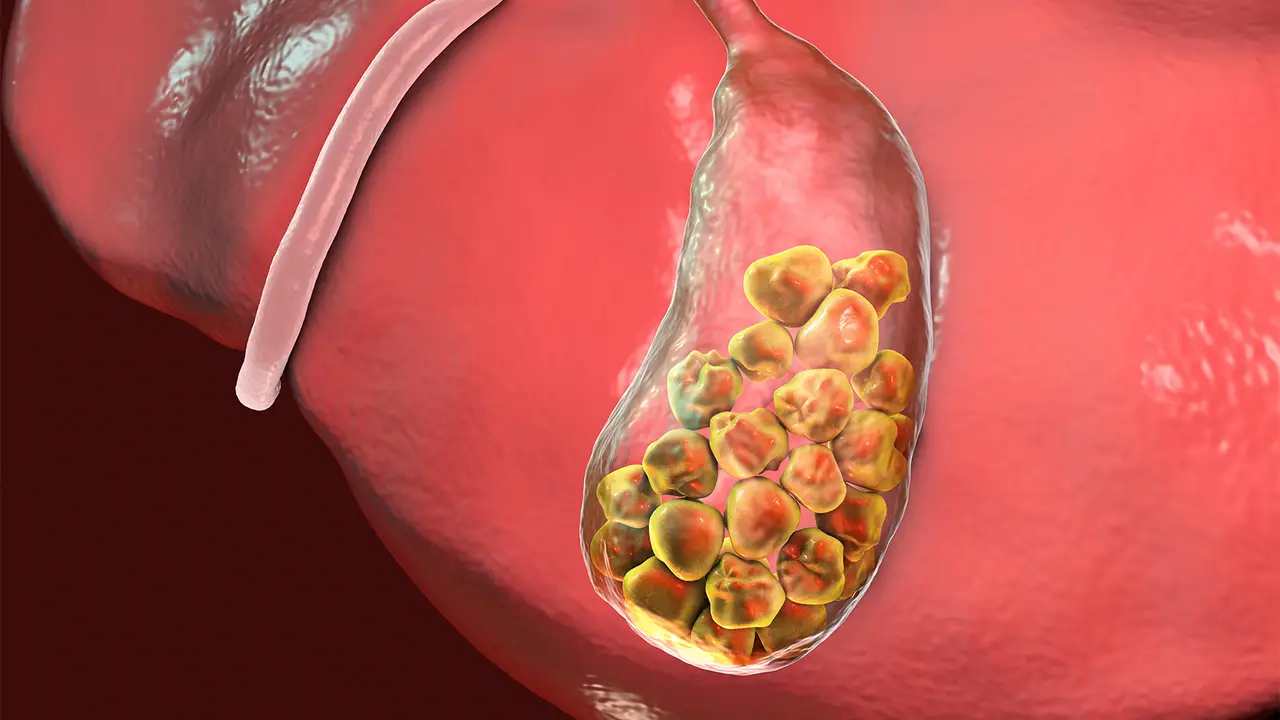
Gallstones are small, hard particles that form in the gallbladder. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid. When there is too much cholesterol or bilirubin, stones may form. Gallstones can vary in size and cause a range of symptoms. Some children may not experience any symptoms, while others can face serious discomfort. Gallstones can block bile ducts, leading to pain and infection.
Gallstones in children may develop due to various factors. Obesity is one of the leading causes. Children with higher body fat are at greater risk. Diet also plays a significant role in gallstone formation. A diet high in fats and low in fiber can increase the risk. Genetics can also influence gallstone development. Children with a family history of gallstones may be more susceptible.
Certain medical conditions can contribute to the formation of gallstones. For example, children with sickle cell anemia or cystic fibrosis are at higher risk. Infections of the gallbladder or bile ducts can also lead to gallstone development. These conditions may interfere with the normal function of the gallbladder, causing bile to become more concentrated.
“Read about: Exclusive Breastfeeding: A Key to Your Baby’s Health and Immunity”
Many children with gallstones do not show symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can be severe. The most common symptom is abdominal pain. The pain is usually located in the upper right side of the abdomen. It may occur after eating, especially after a fatty meal. Some children may also experience nausea or vomiting. If the stones block a bile duct, it can lead to jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
In some cases, the pain may be intermittent, coming and going. If a child experiences constant pain or if the pain worsens, it’s important to seek medical attention. Other symptoms may include fever or chills, indicating an infection of the gallbladder. Severe symptoms should not be ignored, as untreated gallstones can lead to complications.
Diagnosing gallstones in children typically involves a physical examination. The doctor will ask about the child’s symptoms and medical history. To confirm the diagnosis, imaging tests are usually required. Ultrasound is the most common method for detecting gallstones. It is non-invasive and can clearly show the presence of stones in the gallbladder. In some cases, additional tests such as CT scans or MRIs may be used.
Blood tests may also be performed to check for signs of infection or liver dysfunction. These tests can help determine if the gallstones are causing complications, such as bile duct obstruction.
“Read more: Preventing Tetanus in Children: Vaccination and Safety Tips”
Treatment for gallstones in children depends on the severity of the condition. If the child is not experiencing significant symptoms, the doctor may recommend a watch-and-wait approach. In many cases, gallstones may not cause major problems and may not require immediate treatment.
For children with severe symptoms or complications, surgery may be necessary. The most common surgical procedure is cholecystectomy, which involves the removal of the gallbladder. This procedure is often done laparoscopically, which is minimally invasive. The child can usually go home the same day or the following day. In cases where surgery is not an option, medication may be used to dissolve the gallstones, although this is less common.
In some cases, if the gallstones cause a blockage or infection, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed. The child may need to stay in the hospital for a short period until the infection is under control. Follow-up care is essential to ensure the child’s recovery and to monitor for any further issues.
While not all cases of gallstones can be prevented, there are steps that can reduce the risk. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. Encouraging children to eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help. Limiting high-fat foods and sugary drinks can prevent weight gain and reduce the likelihood of gallstone formation.
Regular physical activity is also important. Encouraging children to be active can help maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity. If the child has a family history of gallstones, it is important to monitor their health and seek medical advice if symptoms arise.