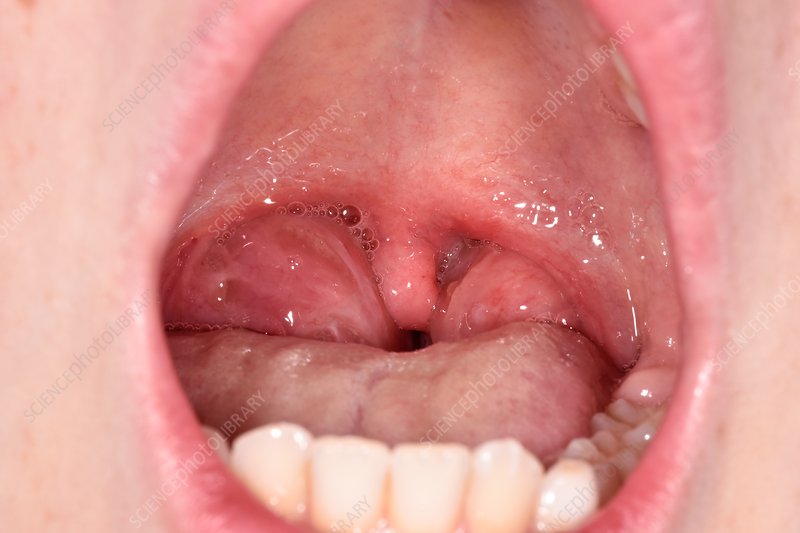
Not to be used for advertising or in a defamatory context Tonsillitis in a child. Swollen and inflamed tonsils in the throat of a 10-year-old boy. Tonsillitis is usually caused by an infection by streptococci bacteria, in this case a group B streptococcus infection. Tonsils are oval-shaped masses of spongy lymphoid tissue on either side of the back of the mouth. They play a role in the body's response to infection, producing antibodies for the immune system and trapping and destroying micro-organisms that enter the throat. Tonsillitis causes a sore throat, fever and difficulty with swallowing. Treatment involves a course of antibiotic drugs. If it is recurrent and severe, then the tonsils may need to be surgically removed (tonsillectomy).
DiYES International School – Tonsillitis in children is a common condition that parents often encounter. It involves inflammation of the tonsils, the two lymph nodes located at the back of the throat. While tonsillitis can be caused by both viral and bacterial infections, it often causes concern due to its symptoms. In this article, we will discuss the signs that indicate when to seek medical attention for tonsillitis in children.
Tonsillitis occurs when the tonsils become inflamed, usually due to an infection. The inflammation can result in a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, and swollen tonsils. In some cases, the tonsils may have visible white or yellow patches. It is important to differentiate between viral and bacterial tonsillitis, as bacterial tonsillitis may require antibiotics for proper treatment.
“Read about: Relieving Gastritis Symptoms in Children: A Practical Approach”
The symptoms of tonsillitis can vary depending on whether the infection is viral or bacterial. Some common signs include:
While mild cases of tonsillitis can be managed at home, there are certain situations when medical attention is necessary. Parents should seek professional help if:
Treatment for tonsillitis depends on whether the infection is viral or bacterial. Viral tonsillitis usually resolves on its own, and the treatment focuses on symptom relief. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help reduce pain and fever. Saltwater gargles, throat lozenges, and plenty of fluids also aid in soothing a sore throat.
For bacterial tonsillitis, doctors typically prescribe antibiotics. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Untreated bacterial tonsillitis can lead to complications, such as rheumatic fever or kidney problems.
In severe or recurrent cases of tonsillitis, a doctor may recommend a tonsillectomy, which is the surgical removal of the tonsils. This option is usually reserved for children who have frequent infections or complications related to their tonsils.
“Read more: Natural Remedies for Swollen Gums in Kids: What You Can Do”
While tonsillitis cannot always be prevented, there are a few steps parents can take to reduce the risk of infection:
In rare cases, children may experience recurrent tonsillitis. This can significantly affect their quality of life and may require surgical intervention. A tonsillectomy may be recommended if a child experiences:
Parents should discuss the risks and benefits of a tonsillectomy with their child’s healthcare provider to make an informed decision.