DiYES International School – Scabies in children can cause a great deal of discomfort, often leading to constant itching and irritation. Scabies is a skin condition caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin. These mites lay eggs, leading to inflammation and an intense itching sensation. While it is common in children, it can affect anyone. Early detection and treatment are crucial in providing relief and preventing further spread. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for scabies in children.
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which burrows into the outer layer of the skin. These mites are extremely small and often go unnoticed until symptoms appear. Children can get scabies through close contact with an infected person, such as during play or by sharing items like towels or bedding. Scabies can spread quickly in environments like schools and daycare centers, where children are in close contact with each other.
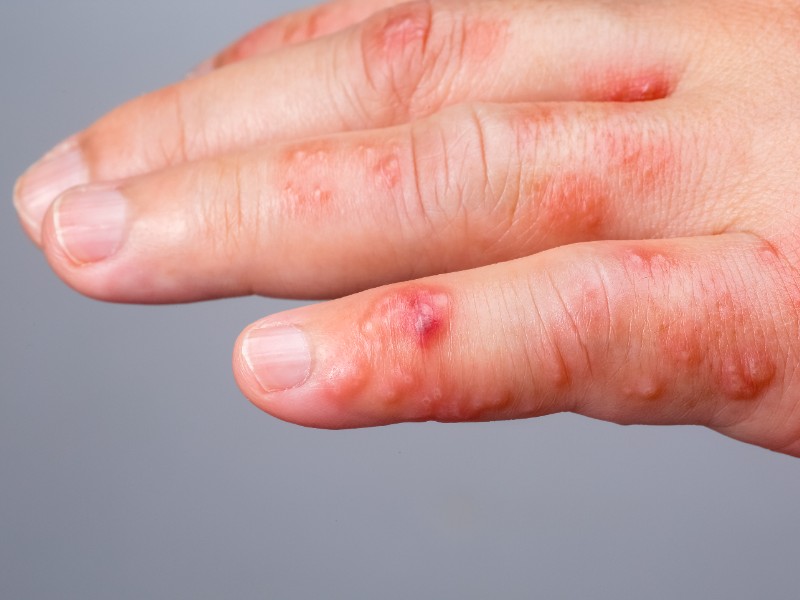
The mites thrive in warm and moist areas of the body, including the wrists, elbows, and between the fingers. Once the mites burrow under the skin, they begin to lay eggs, causing the body to react with irritation, redness, and itching.
“Read about: How to Identify Allergies in Children: A Parent’s Guide”
The primary symptom of scabies in children is itching, which usually becomes more intense at night. The rash often starts as small, red bumps or blisters that can appear in clusters. These can develop into scaly patches or sores, especially from scratching. In severe cases, the skin may become thickened or crusted.
Other common signs of scabies in children include:
Effective treatment for scabies in children typically involves prescription creams or ointments that kill the mites. The most commonly prescribed treatment is permethrin cream, which is applied directly to the skin. This cream needs to be applied from the neck down and left on for a specified period, usually overnight. After the treatment time, the cream should be washed off thoroughly.
In some cases, a doctor may prescribe oral medications like ivermectin, especially if the child has a more severe case of scabies or if topical treatments fail. It is important to follow the doctor’s instructions and complete the entire treatment course, even if symptoms begin to improve.
“Read more: What Parents Need to Know About Impetigo in Children”
To prevent scabies from spreading, it is essential to practice good hygiene. Teach children to wash their hands regularly, avoid sharing personal items, and not engage in close physical contact with someone who has scabies. Children who have scabies should stay home from school or daycare until they complete their treatment and the itching begins to subside. This helps prevent the condition from spreading to other children.
It is also important to keep a child’s skin clean and moisturized to help reduce irritation. Applying a gentle, hypoallergenic moisturizer after treatment can help soothe the skin and prevent excessive dryness.
In some cases, scabies in children can lead to complications such as skin infections from excessive scratching. If the child develops a fever, the rash becomes infected, or the symptoms persist despite treatment, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can evaluate the condition and provide further guidance on managing scabies or addressing any complications that may arise.
Scabies in children is a highly treatable condition. With the right care and treatment, most children will recover fully without any long-term effects. Parents should be vigilant in identifying symptoms early and seek prompt treatment to prevent further spread. By practicing good hygiene, following prescribed treatments, and taking precautions, scabies can be effectively managed and prevented.